Dr. Kwan Mo-You publishes new work in Nano Select on Pickering W/W emulsions stabilized by Alternative Protein Microgels
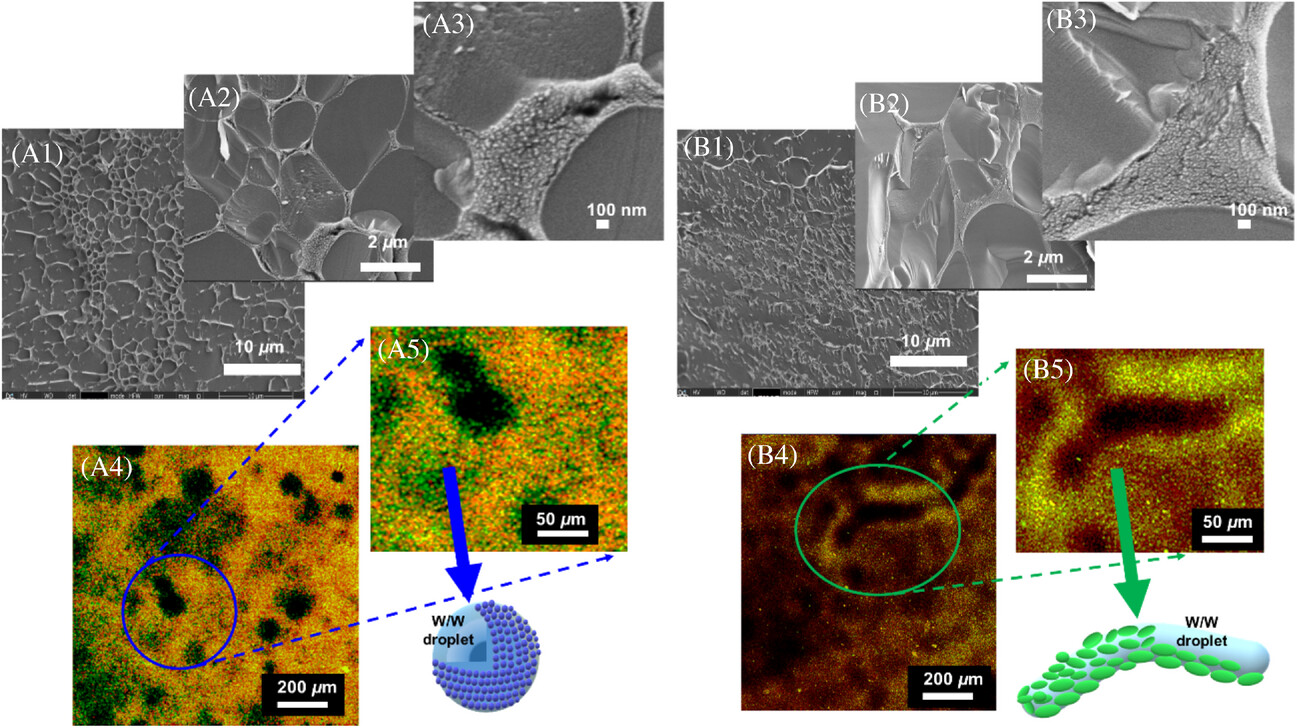
Aqueous multiphasic systems have attracted a great deal of interest recently owing to the growing demands of #sustainability for the development of stable “oil-free” (water-in-water, W/W) emulsions, often complicated by their limited stability against droplet coarsening. In our new paper published in Nano Select led by Dr. Kwan-Mo You (PhD Student, ERC LubSat Project) in collaboration with School of Physics, we show that alternative proteins such as pea protein can be used to create sustainable microgels that can be used to stabilize Pickering W/W emulsions with improved lubrication performance. Strikingly, the microgel and microgel-stabilized-W/W emulsion performances with improved lubricity are in sharp contrast to the behavior of the parent alternative proteins, where pea protein was known to result in increased friction as compared to dairy proteins - Thanks to the interesting material behaviour of these plant protein microgels at colloidal and nanometric length scales. The novel approach of fabricating W/W emulsions stabilized by sustainable alternative protein microgels opens up new solutions in designing aqueous lubricants for future nutritional and biomedical applications. Read the full text here with details on rheology, tribology, nanoscale adhesion measurements, atomic force microscopy (AFM), quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D), multiscale microscopic analyses and much more: https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202300160
