New Food and Function paper on Biopolymer-coated Pickering emulsions
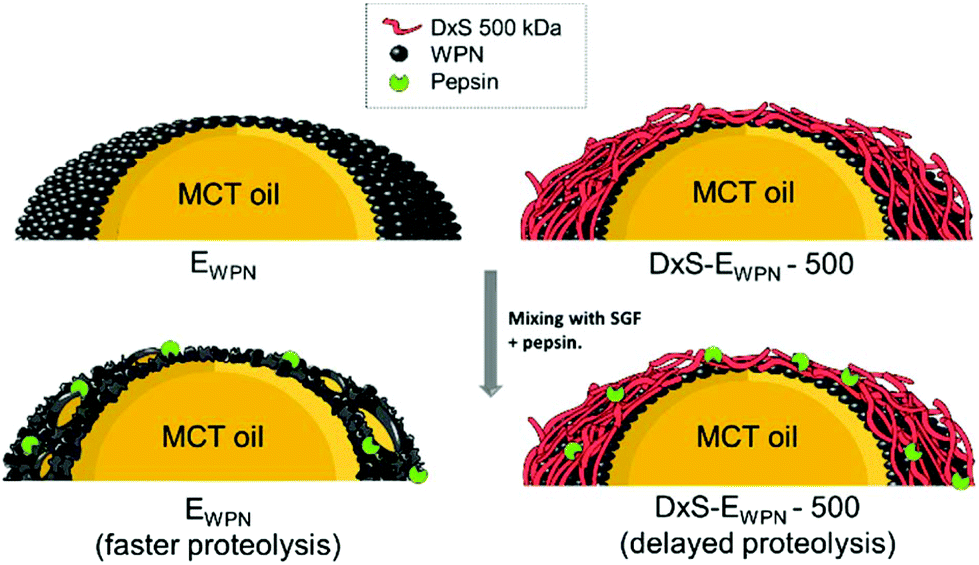
Andrea Araiza-Calahorra (PhD Student) designed new biopolymer-coated Pickering emulsions and demonstrated that such complex biopolymer-coated nanogel-laden interface can be helpful in preventing gastric destabilization of droplets, the study has been published in Food & Function, Volume 10, Pages 5498-5509. Pickering emulsions prepared using whey protein nanogel particles were coated by a layer of anionic polysaccharide, dextran sulphate (DxS) of molecular weight (MW) of 40 or 500 kDa, respectively. The hypothesis was that DxS coating on the protein nanogel particle–laden interface would act as a steric barrier against interfacial proteolysis of the protein nanogel particles by pepsin. Indeed emulsions coated with DxS-500 kDa presented stable droplets with lower rate and degree of pepsin hydrolysis of the adsorbed particulate layer as compared to those coated with DxS-40 kDa or uncoated protein nanogel-stabilized interface after 120 min of gastric digestion, highlighting the importance of charge density and molecular weight of the biopolymer coating. Insights from this study could enable creating future gastric-stable emulsions for food and pharmaceutical applications targeting altered lipid digestion profile in the intestinal phase or encapsulation of lipophilic bioactive compounds that need to be delivered to intestines without any gastric destabilization. Click here to read the paper: https://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01080G
